How do global trade flows impact what ends up on our dinner tables?
Agricultural products crisscross the globe with astonishing frequency, shaping economies and influencing diets worldwide. As the global trade value in agricultural commodities has quadrupled over the past two decades, understanding these trade flows becomes essential.
Who's at the center of these vast economic currents?
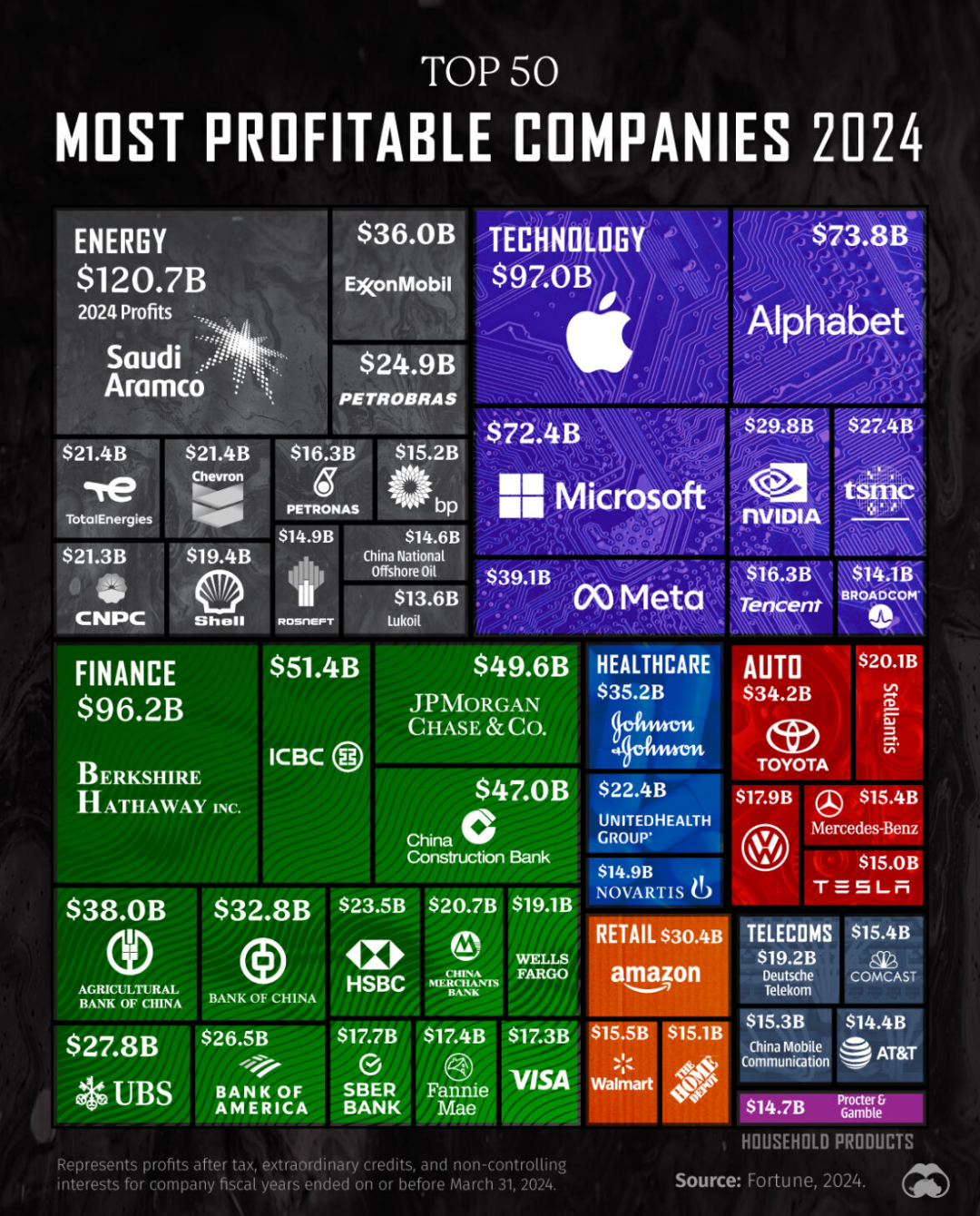
China has emerged as a key player in importing countries, affirming its vital role in the trade of essential commodities. To truly grasp the largest trade flows of agricultural products, one must explore the intersecting pathways of exporting and importing giants. Discover the intricacies of these massive trade networks and their implications in this insightful analysis.
Understanding the Largest Trade Flows of Agricultural Products
Trade flows in agriculture are vital to the global economy, serving as the lifeline for food security and economic development across nations. Why are trade flows important in agriculture? They ensure the distribution of essential commodities from regions of surplus to those of deficit, facilitating market stability and economic growth. By enabling countries to specialize in producing commodities where they have a comparative advantage, trade flows enhance efficiency and productivity in the agricultural sector. This interconnectedness not only supports the livelihoods of millions of farmers but also helps stabilize food prices globally.
How has global agricultural trade grown over the years? The global trade value in agricultural commodities has increased fourfold over the past two decades. This remarkable growth is driven by rising demand, technological advancements, and improved trade agreements. The expansion of global supply chains and the integration of emerging markets into the world economy have also contributed to this trend. As economies grow and consumer preferences shift toward diverse and high-quality food products, international trade becomes a critical component in meeting these demands.
Which countries are key players in agricultural trade flows? Major exporting and importing countries are pivotal in shaping these trade dynamics. For instance, the United States, Brazil, and the European Union are leading exporters of agricultural products, leveraging their vast resources and technological capabilities. On the other hand, China has emerged as a significant importer, driven by its large population and increasing food consumption. China's role exemplifies how economic growth and changing dietary patterns in populous nations can significantly influence global trade flows, underscoring the interconnected nature of the world's agricultural markets.
Major Exporters and Importers in Global Agriculture Trade
Why are major exporters and importers important in global agriculture trade? They are the backbone of international markets, facilitating the movement of essential agricultural commodities worldwide. Major exporters provide the necessary supply for countries that cannot produce specific goods efficiently, while major importers ensure that these products reach consumers who demand them. This dynamic not only supports global food security but also enables countries to focus on producing goods where they have a competitive advantage, thus enhancing global economic stability.
- Soybeans (Brazil to China)
- Vegetables (Mexico to China)
- Fruits and Berries (Mexico to China)
- Meat: Beef (Brazil to China)
- Rubber and Gums (Thailand to China)
- Wheat (U.S. to China)
- Meat: Pork (U.S. to China)
- Palm Oil and Kernels (Indonesia to China)
- Other Edible Oils (Malaysia to China)
- Maize (U.S. to China)
Who are the major exporters of agricultural products? Brazil, the United States, and Thailand are key players. Brazil is a leading exporter of soybeans and beef, leveraging its vast arable land and favorable climate. The United States exports a variety of products, including maize and pork, benefiting from advanced agricultural technology and infrastructure. Thailand is known for its rubber and gums, capitalizing on its tropical climate. These countries play critical roles in meeting the global demand for diverse agricultural products, ensuring that international markets remain well-supplied.
Which countries are the major importers of agricultural commodities? China stands out as the primary importer, especially of soybeans, meat, and wheat. With a large and growing population, China's demand for these commodities is immense, driven by increasing urbanization and changing dietary preferences. Importing from countries like Brazil and the U.S., China secures its food supply and supports its domestic consumption needs. This reliance on imports underscores the significance of international trade partnerships and their impact on global agricultural markets.
Economic Impacts of Agricultural Trade Flows
What are the general economic benefits of trade flows? Trade flows in agriculture foster economic growth by providing access to a broader range of markets and resources. They enable countries to export surplus products, thereby enhancing their economic stability. By facilitating specialization, trade flows contribute to increased productivity and efficiency, allowing nations to focus on producing goods where they have a comparative advantage. Additionally, these flows support job creation in sectors like farming, logistics, and processing, boosting overall economic health.
How do trade conflicts negatively impact agricultural trade? The 2018-2019 U.S.-China trade conflict illustrates substantial negative impacts, with U.S. agricultural exports to China dropping by $10.7 billion. Trade conflicts disrupt established supply chains and create uncertainty, leading to decreased export volumes and financial losses for producers. They can also result in retaliatory tariffs, further hindering market access and competitiveness. Such conflicts not only affect immediate trade relationships but can also have long-term repercussions on international agricultural trade dynamics.
How do competing countries benefit from trade conflicts? Competing countries often seize opportunities to capture market share when trade conflicts arise. During the U.S.-China conflict, nations like Brazil and Australia/New Zealand increased their exports to China, filling the gap left by the U.S. These countries benefit from the increased demand for their products, which can lead to expanded production capacities and strengthened trade relationships. This shift underscores the importance of adaptability and strategic positioning in the global agricultural market.
| Trade Conflict | Impact on Exports | Competing Countries Benefit |
|——————————|——————————-|———————————-|
| U.S.-China Trade Conflict | $10.7 billion drop in exports | Brazil, Australia/New Zealand |
| EU-Russia Trade Sanctions | Decreased EU exports | Argentina, Turkey |
| India-Pakistan Trade Tensions| Reduced bilateral trade | Bangladesh, Vietnam |
Factors Influencing Trade Flows of Agricultural Products
How do supply chain logistics affect trade flows? Efficient supply chain logistics are crucial for the smooth movement of agricultural products across borders. They determine the speed and cost-effectiveness with which goods can reach their destination. The importance of logistics in trade flows is that they ensure timely delivery and minimize spoilage, particularly for perishable goods like fruits and vegetables. Well-developed infrastructure, such as ports and transportation networks, plays a significant role in reducing delays and enhancing trade efficiency. Conversely, inadequate logistics can lead to bottlenecks, increasing costs and reducing competitiveness in international markets.
What impact do market trends have on trade flows? Market trends significantly influence the demand and supply dynamics of agricultural products. The influence of market trends includes shifts in consumer preferences, such as the increasing demand for organic and sustainably sourced products, which can alter the types and quantities of goods traded. Seasonal variations and climatic conditions also affect crop yields, influencing trade volumes and prices. Additionally, global economic conditions, such as recessions or booms, impact purchasing power and, consequently, the demand for imported goods. Staying attuned to these trends is essential for producers and exporters to adapt and remain competitive.
How do trade policies shape agricultural trade flows? Trade policies, including tariffs, quotas, and bilateral agreements, have a direct impact on trade flows. The role of trade policies is to either facilitate or hinder the movement of goods. Tariffs can increase the cost of imported goods, affecting competitiveness, while trade agreements may lower barriers, promoting increased trade volumes. Policies aimed at protecting domestic industries can lead to retaliatory measures, impacting global trade dynamics. Understanding and navigating these policies is crucial for countries to maintain favorable trade relationships and optimize their agricultural exports and imports.
- Tariffs and trade policies
- Infrastructure and logistics
- Market demand and price volatility
- Supply chain disruptions
- Technological advancements
The Role of Trade Agreements and Partnerships
Why are trade agreements important in agriculture? Trade agreements are essential for reducing barriers that hinder the flow of agricultural products between countries. How do they achieve this? By lowering tariffs, eliminating quotas, and setting standardized regulations, trade agreements facilitate smoother and more predictable trade. This not only increases market access for exporters but also reduces costs for importers, promoting a more competitive and efficient global agricultural market. As a result, countries can engage in mutually beneficial exchanges, enhancing food security and economic stability.
Which key trade partnerships significantly impact agricultural trade? Notable partnerships, such as the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and the European Union's Common Agricultural Policy (CAP), exemplify the benefits of cooperative trade arrangements. What benefits do they offer? These partnerships streamline cross-border trade by establishing common standards and procedures, thus reducing transaction costs and fostering closer economic ties. By aligning policies and practices, trade partnerships enable countries to leverage each other's strengths, facilitating the exchange of diverse agricultural goods and services.
How do trade agreements enhance global supply chains? Trade agreements integrate into global supply chains by ensuring the seamless movement of goods across borders. In what ways do they enhance supply chains? By providing a stable framework for trade, agreements help mitigate risks associated with political and economic uncertainties. They also encourage investment in infrastructure and technology, improving logistics and distribution networks. This integration not only boosts the efficiency of supply chains but also enhances their resilience, enabling them to adapt to shifting market demands and global challenges.
Final Words
In reviewing the intricate web of global agricultural trade, it's evident that the largest trade flows of agricultural products have reshaped economies and international relationships.
The significant growth in global trade, driven by major importing nations like China, highlights the importance of key exporters such as the U.S. and Brazil.
Understanding the economic impacts and factors influencing these trade flows, from trade conflicts to logistics, reveals how crucial adaptation is in the current landscape.
Ultimately, robust trade agreements and partnerships are critical for minimizing barriers and supporting market access across global supply chains.
Navigating these dynamics promises not only challenges but also opportunities for innovation and economic expansion.