Is the U.S. trade deficit a sign of economic strength or weakness?
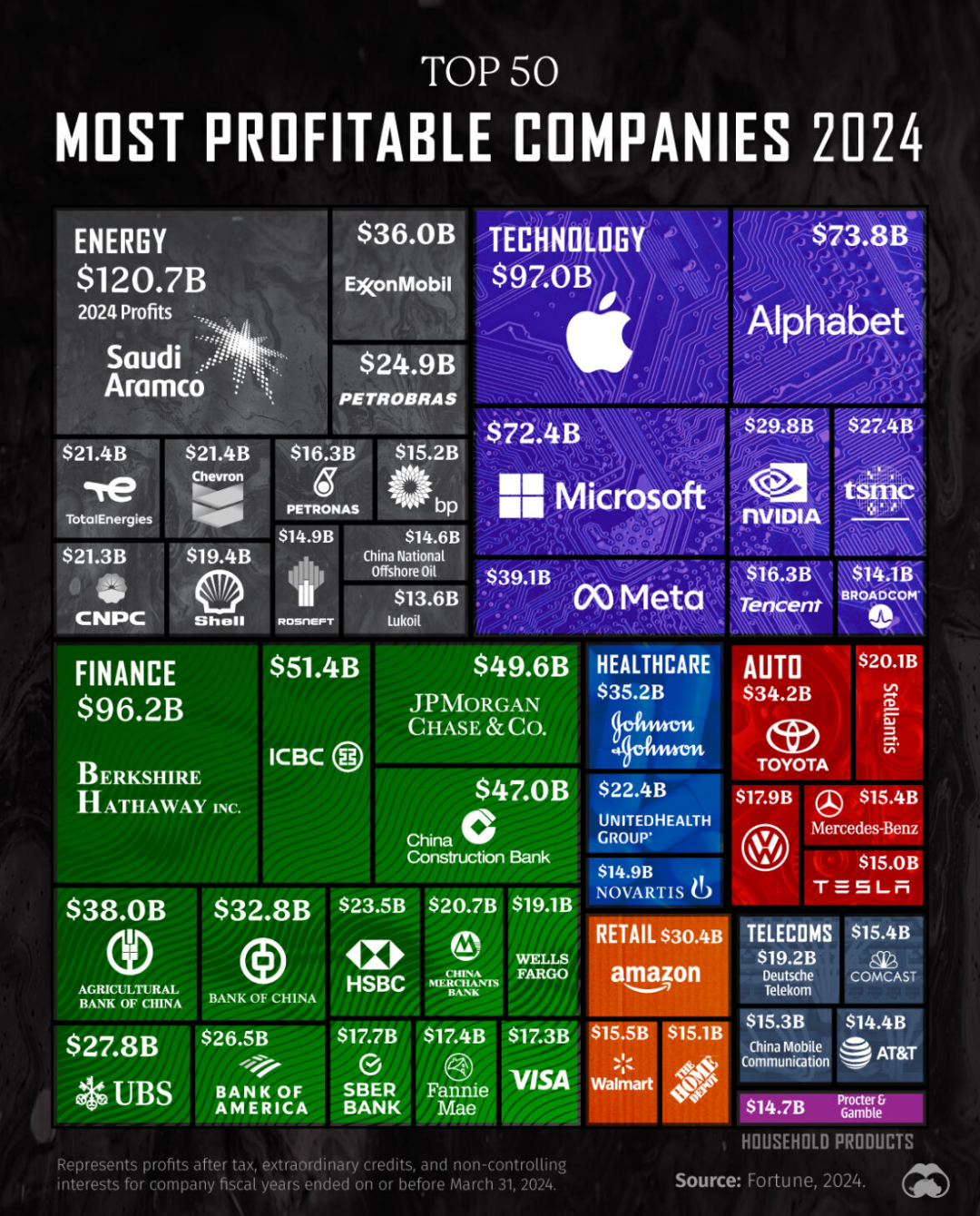
The U.S. trade deficit in 2023 witnessed a positive shift, dropping to $779.8 billion from $951.2 billion in 2022. This change was driven by a decrease in the goods deficit by $121.3 billion and an increase in the services surplus of $56.4 billion.
This article explores these developments, analyzing the contributing factors and placing them in historical context to uncover what these shifts mean for the U.S. economy.
For those seeking to understand the current economic landscape and its implications, the insights provided here are essential.
Overview of the U.S. Trade Deficit in 2023
The U.S. trade deficit experienced a notable improvement in 2023, declining to $779.8 billion from $951.2 billion in 2022. This positive shift represents a significant reduction, marking a year of economic adjustments and strategic trade management. The decrease is a clear indicator of the nation's evolving trade dynamics and economic policies aimed at balancing imports and exports.
Key changes were observed within the components of the trade deficit, particularly in the goods deficit and services surplus. The goods deficit saw a substantial decrease of $121.3 billion, bringing it down to $1,061.7 billion. This decline suggests a more favorable balance in the trade of physical products, possibly due to enhanced export strategies or reduced import dependency. On the other hand, the services surplus increased by $56.4 billion, reaching a total of $288.2 billion. This increase highlights the growing strength and competitiveness of U.S. services in the global market, contributing positively to the overall trade balance.
In relation to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), the trade deficit represented 2.8 percent of the current-dollar GDP in 2023, down from 3.7 percent in 2022. This reduction underscores the trade deficit's lessening impact on the broader U.S. economy, reflecting an improvement in economic health. The lowered percentage signifies a more sustainable trade environment, aligning with national economic goals and fostering a more robust economic outlook.
Factors Contributing to the U.S. Trade Deficit in 2023
The U.S. trade deficit in 2023 experienced a significant reduction, largely due to an increase in exports and a decrease in imports. This shift is indicative of a more balanced trade relationship, where the U.S. has successfully enhanced its export capabilities while managing import levels. The improved export performance can be attributed to competitive pricing and innovation in key industries, while the decline in imports suggests a strategic move towards self-reliance and domestic growth.
Key factors influencing these changes include:
- Consumer Demand: Shifts in domestic and international consumer preferences affected both import and export volumes.
- Exchange Rates: Fluctuating exchange rates made U.S. exports more attractive and imports more expensive.
- Global Economic Conditions: Economic recovery in various regions increased demand for U.S. goods and services.
Consumer demand played a pivotal role in shaping the trade deficit dynamics. With an evolving preference for U.S.-made products, domestic consumption saw a boost, thereby reducing reliance on imported goods. Additionally, the exchange rate fluctuations provided a competitive edge to U.S. exports, making them more affordable to international buyers and discouraging import consumption due to higher costs. These monetary dynamics helped tilt the balance in favor of exports, contributing to the overall deficit reduction.
The broader global economic conditions also had a substantial impact. As economies worldwide began recovering from previous downturns, demand for U.S. goods and services surged. This global rebound created a fertile ground for U.S. exporters to expand their market share and capitalize on new opportunities. The interplay of these economic indicators illustrates how external and internal factors collectively influenced the trade deficit, highlighting the intricate nature of international trade relations.
Historical Context and Trends of the U.S. Trade Deficit
The U.S. trade deficit has evolved significantly over the decades, marked by pivotal economic and political events. From 1990 to 2024, the trade deficit has experienced notable shifts, particularly with major trade partners like China. The infographic data highlights a 28% decline in the trade deficit with China, contrasted by a 96% surge with the rest of the world. This trend underscores a diversification in trade relations and a shift in global economic dynamics. The historical context reveals how strategic and geopolitical factors have influenced trade balances, contributing to the current state of the U.S. economy.
| Year | Event | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2001 | China’s accession to the WTO | Increased trade with China, leading to a higher trade deficit |
| 2008 | Global financial crisis | Trade deficits peaked due to reduced global demand |
| 2018 | U.S.-China trade war | Temporary reduction in trade deficit with China |
| 2020 | COVID-19 pandemic | Trade deficits peaked again due to disrupted supply chains |
Analyzing trends leading up to 2023, it's evident that the U.S. has been navigating a complex trade landscape, shaped by both internal policies and external pressures. The decline in the trade deficit with China suggests a strategic pivot towards diversifying trade relations, while the surge with other global partners indicates a broadening of the U.S. export market. These trends highlight the ongoing adjustments in trade policies and economic strategies aimed at fostering a more balanced and sustainable trade environment. As the U.S. continues to adapt to global economic shifts, understanding these historical trends is crucial for anticipating future trade developments.
Economic Implications of the U.S. Trade Deficit
The U.S. trade deficit plays a pivotal role in shaping the currency value. When a country imports more than it exports, it often results in a depreciation of its currency. This happens because increased demand for foreign currencies to pay for imports can weaken the domestic currency. In 2023, the reduced trade deficit helped support the U.S. dollar, contributing to a more stable exchange rate environment. A stronger dollar can reduce inflationary pressures by making imported goods cheaper, benefiting consumers and businesses alike.
The trade deficit also significantly impacts employment and GDP. A persistent deficit can lead to job losses in manufacturing sectors as domestic production is often outcompeted by cheaper imports. However, the 2023 reduction in the trade deficit signals a shift towards more balanced trade, which can help preserve and even create jobs in key industries. Furthermore, a lower trade deficit can contribute positively to GDP growth by increasing net exports, a crucial component of the GDP calculation. This improvement in trade balance suggests a healthier economic structure, supporting sustained economic expansion.
Looking at the broader U.S. economic outlook, the reduction in the trade deficit presents both opportunities and challenges. On the one hand, it reflects an improving economic health, with potential for increased investment and consumption. On the other hand, maintaining this positive trend requires navigating global trade uncertainties and domestic policy adjustments. Potential challenges include geopolitical tensions, evolving trade agreements, and shifts in global demand. Addressing these issues will be essential for sustaining the economic gains achieved in 2023 and ensuring long-term growth.
U.S. Trade Policies and Future Outlook
Current U.S. trade policies are strategically designed to enhance economic growth and strengthen international trade relations. These policies focus on reducing trade barriers, promoting fair trade practices, and ensuring a level playing field for U.S. businesses. The objectives are to boost exports, protect domestic industries, and foster economic resilience in a competitive global market.
Key policies include:
- Tariff Adjustments: Modifying tariffs to protect strategic industries while encouraging imports of essential goods.
- Trade Agreements: Negotiating new trade deals and revisiting existing ones to ensure mutual benefits and access to foreign markets.
- Export Incentives: Providing support to U.S. businesses through financial aid and resources to increase their presence in global markets.
Looking ahead, the U.S. trade outlook is influenced by evolving global economic conditions and domestic policy shifts. As trade forecasts suggest a gradual recovery in global demand, the U.S. aims to capitalize on these opportunities by reinforcing its trade agreements and adjusting policies to address emerging challenges. Policy adjustments will play a crucial role in shaping the trade deficit's trajectory, ensuring it aligns with broader economic goals. By adapting to changing circumstances, the U.S. can maintain a positive trade balance and support sustained economic growth.
Final Words
Analyzing the U.S. trade deficit in 2023 offers insightful perspectives on the nation's economic health.
The deficit decreased significantly to $779.8 billion, improving from 2022's $951.2 billion.
This change is driven by reduced goods deficits and an increase in the services surplus, reflecting evolving trade dynamics.
Identifying factors such as increased exports, decreased imports, and economic conditions is crucial for understanding this shift.
Historically, the U.S. trade deficit has fluctuated due to events like China's WTO accession and the financial crisis.
Evaluating economic implications, the trade deficit notably affects currency value, employment, and GDP.
Future trade policies are expected to continue influencing the U.S. trade outlook, emphasizing the role of strategic adjustments.
U.S. trade deficit analysis 2023 provides a window into economic trends and potentials, underscoring the importance of staying informed and adaptable for future developments.