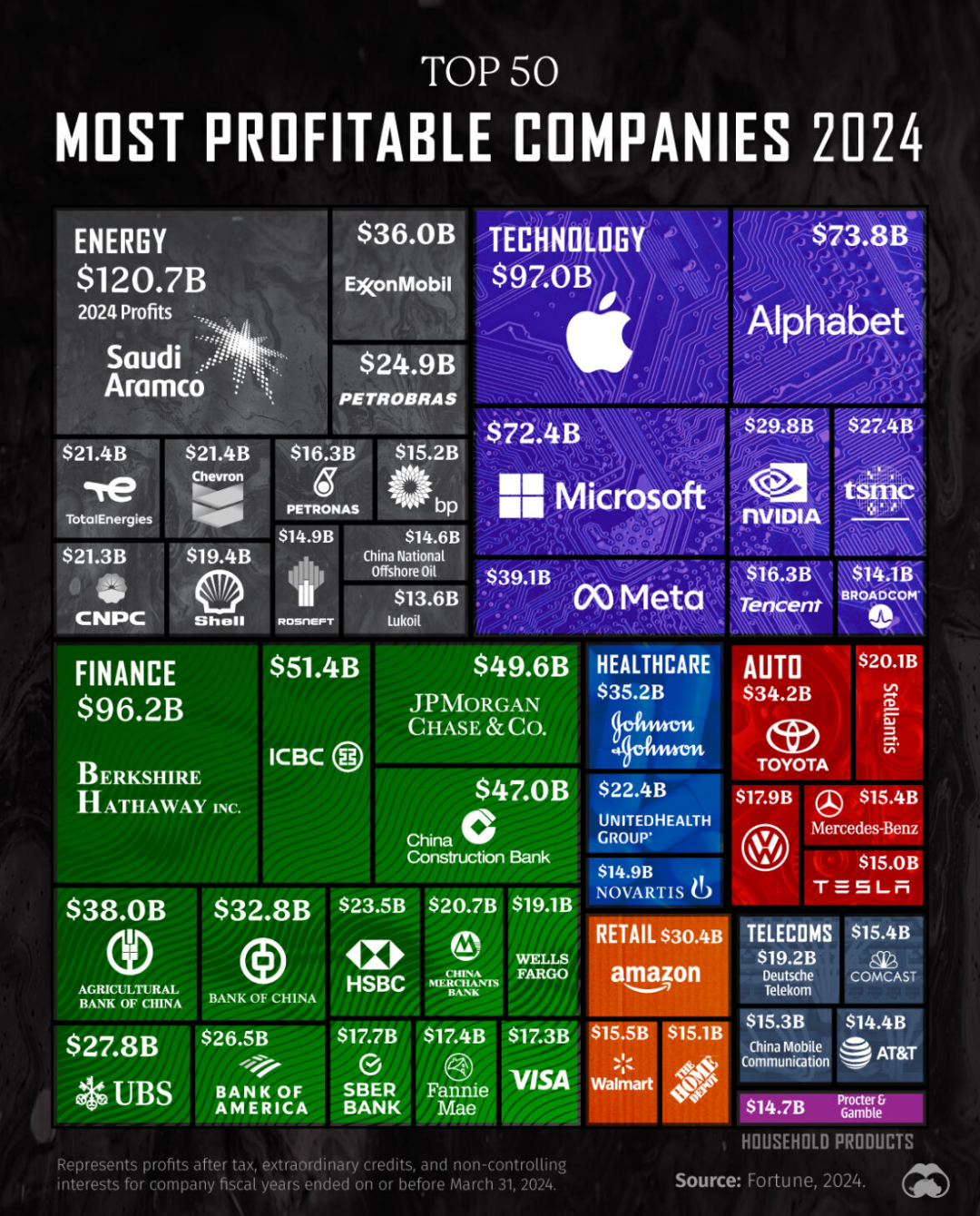
Is it hot enough for you? As global temperatures continue to rise, understanding the historic highs in different countries becomes crucial.
From Death Valley, California, to the searing heat of Ahvaz, Iran, every continent showcases its own temperature extremes—each telling a unique story about its climate and geography. But why is it important to discuss these record-breaking temperatures?
Examining these highs not only unravels patterns of climate change but also highlights the potential impacts on societies and economies worldwide.
In this article, take a closer look at the highest temperatures ever recorded by country and uncover what they mean for our planet.
What is the highest temperature ever recorded? It was an extreme 56.7°C (134°F) in Death Valley, California, USA.
Record High Temperatures by Continent
Understanding extreme temperatures by continent is crucial for grasping the global patterns of heat distribution. These records highlight the intensity and frequency of extreme weather events, which can have profound implications on ecosystems and human activities. For instance, North America's Death Valley, California, holds the record for the highest temperature, reaching a scorching 56.7°C (134°F) in 1913. Such records not only illustrate the geographical diversity of heat extremes but also underscore the importance of monitoring and adapting to these unprecedented conditions.
| Continent | Location | Temperature | Year |
|————-|————————|————-|——|
| North America | Death Valley, California, US | 56.7°C | 1913 |
| South America | Rivadavia, Argentina | 48.9°C | 1905 |
| Europe | Sicily, Italy | 48.8°C | 2021 |
| Africa | Kebili, Tunisia | 55°C | 1931 |
| Asia | Ahvaz, Iran | 54°C | 2017 |
| Oceania | Oodnadatta, Australia | 50.7°C | 1960 |
| Antarctica | Seymour Island | 20.7°C | 2020 |
The reasons behind these temperature extremes vary, ranging from geographical factors to climate change. Regions like Death Valley and Kebili are naturally predisposed to high temperatures due to their geographic and climatic conditions. However, recent records, such as those in Sicily and Ahvaz, point towards a growing influence of global warming. The increase in greenhouse gases and deforestation are contributing to more frequent and severe heatwaves, making it imperative for countries to address these challenges through sustainable practices and policies.
Highest Temperatures Recorded by Country
National temperature records serve as crucial indicators of climatic extremes and provide valuable insights into the changing patterns of our environment. These records not only reflect the severity of heatwaves but also help in understanding regional climatic trends. They are essential for national weather services to improve forecasting models and prepare for future weather events. By examining these temperature highs, we can gain a clearer picture of the potential challenges posed by climate change and the necessary adaptation strategies.
- United States: Death Valley, California – 56.7°C (134°F, 1913)
- Argentina: Rivadavia – 48.9°C (120°F, 1905)
- Italy: Sicily – 48.8°C (119.8°F, 2021)
- Tunisia: Kebili – 55°C (131°F, 1931)
- Iran: Ahvaz – 54°C (129°F, 2017)
- Australia: Oodnadatta – 50.7°C (123.3°F, 1960)
- Mexico: Sonoran Desert – 80°C (detected by NASA)
- India: Phalodi, Rajasthan – 51°C (123.8°F, 2016)
- Pakistan: Turbat – 53.7°C (128.7°F, 2017)
- Kuwait: Mitribah – 54°C (129.2°F, 2016)
The implications of these extreme temperatures are profound, particularly for local climates. Regions experiencing record highs often face intensified heatwaves, which can exacerbate drought conditions and threaten water resources. This can lead to ecological stress, impacting biodiversity and agricultural productivity. In countries like India and Pakistan, where recent records were noted, the rising temperatures are a stark reminder of the need for robust climate resilience strategies to safeguard against future climatic adversities.
From a socioeconomic perspective, extreme temperatures can have far-reaching effects. Increased energy demand for cooling, health risks due to heat-related illnesses, and disruptions in daily life are just a few of the challenges faced by communities. In densely populated areas, the urban heat island effect can amplify these impacts, necessitating comprehensive urban planning and infrastructure adaptation. As global temperatures continue to rise, understanding and addressing these challenges becomes ever more critical for ensuring sustainable development and human well-being.
Global Heat Trends and Patterns
Recent record high temperatures observed in the northern hemisphere underscore broader global trends in climate change. These records, reaching unprecedented levels, highlight the intensifying nature of heatwaves across the globe. For instance, the hottest places on Earth, such as regions in Mexico's Sonoran Desert, are witnessing even more extreme temperatures than before. This pattern not only demonstrates the escalating severity of heat events but also raises critical concerns about the sustainability of current environmental practices.
Climate change plays a significant role in these alarming temperature records. The increase in atmospheric greenhouse gases has been linked to the amplification of heatwaves, particularly in the northern hemisphere. With countries like Mexico experiencing soaring temperatures, it becomes evident that climate change is exacerbating natural heat cycles. These changes result in more frequent and severe weather conditions, posing challenges for ecosystems and human societies alike. As these patterns continue, understanding and adapting to these shifts will be crucial for mitigating the impacts of climate change and ensuring a sustainable future.
Measuring and Verifying Temperature Records
Accurate temperature recording is vital for understanding climate patterns and making informed decisions in various sectors such as agriculture, health, and urban planning. Precise measurements help in creating reliable meteorological records, which are essential for tracking climate change and predicting future weather events. Without accurate data, efforts to mitigate and adapt to climate-related challenges may be compromised.
Meteorological services employ several techniques to measure temperatures accurately. These include the use of thermometers, satellite data, and automated weather stations. Thermometers are often housed in Stevenson screens to shield them from direct sunlight and ensure accurate readings. Satellite technology provides a broader view of temperature variations across large regions, while automated weather stations offer continuous data collection, which is crucial for real-time monitoring.
Verification of temperature records involves a rigorous process to ensure data reliability. This includes cross-referencing measurements from multiple sources, such as comparing satellite data with ground-based observations. Meteorological organizations also conduct regular calibration of instruments and review historical data to identify anomalies. By maintaining stringent verification processes, these organizations ensure that temperature records are both precise and trustworthy, forming the backbone of climate science and policy-making.
Implications and Impacts of Extreme Temperatures
Extreme heatwaves have immediate and severe impacts on societies, particularly concerning public health and infrastructure. The rise in temperatures often leads to an increase in heat-related illnesses, such as heat exhaustion and heatstroke, which can be life-threatening if not promptly addressed. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those with preexisting health conditions, are at a higher risk during these periods. Moreover, the strain on infrastructure, such as power grids and transportation systems, becomes evident as the demand for cooling surges. This can result in power outages and transportation delays, disrupting daily life and economic activities.
In the long term, the implications of record heat are profound and multifaceted. Ecosystems face significant stress as species struggle to adapt to rapidly changing conditions, leading to shifts in biodiversity and the potential extinction of less adaptable species. Agricultural productivity is also impacted, with heatwaves exacerbating drought conditions and reducing crop yields. This can lead to economic challenges for communities dependent on agriculture, increasing food insecurity and driving up prices. Additionally, rising temperatures contribute to the urban heat island effect, where cities become significantly warmer than their rural surroundings, further intensifying the need for sustainable urban planning and climate adaptation strategies. As these patterns persist, it becomes crucial for societies to implement resilient measures to mitigate the far-reaching impacts of extreme temperatures.
Final Words
Through a detailed exploration of record high temperatures by continent and country, the article unveils the extreme conditions shaping our planet.
From North America's Death Valley to Phalodi, India, understanding these records emphasizes their significance in climate study.
Examining global trends, it's evident that climate change intensifies these extremes, creating new patterns that challenge existing norms.
Temperature measurement and verification provide critical insights, ensuring accuracy for informed decision-making.
Recognizing the impacts of such temperature extremes is crucial for developing resilient societies.
The highest temperatures ever recorded by country underscore the reality of our warming world, inspiring action towards a cooler future.