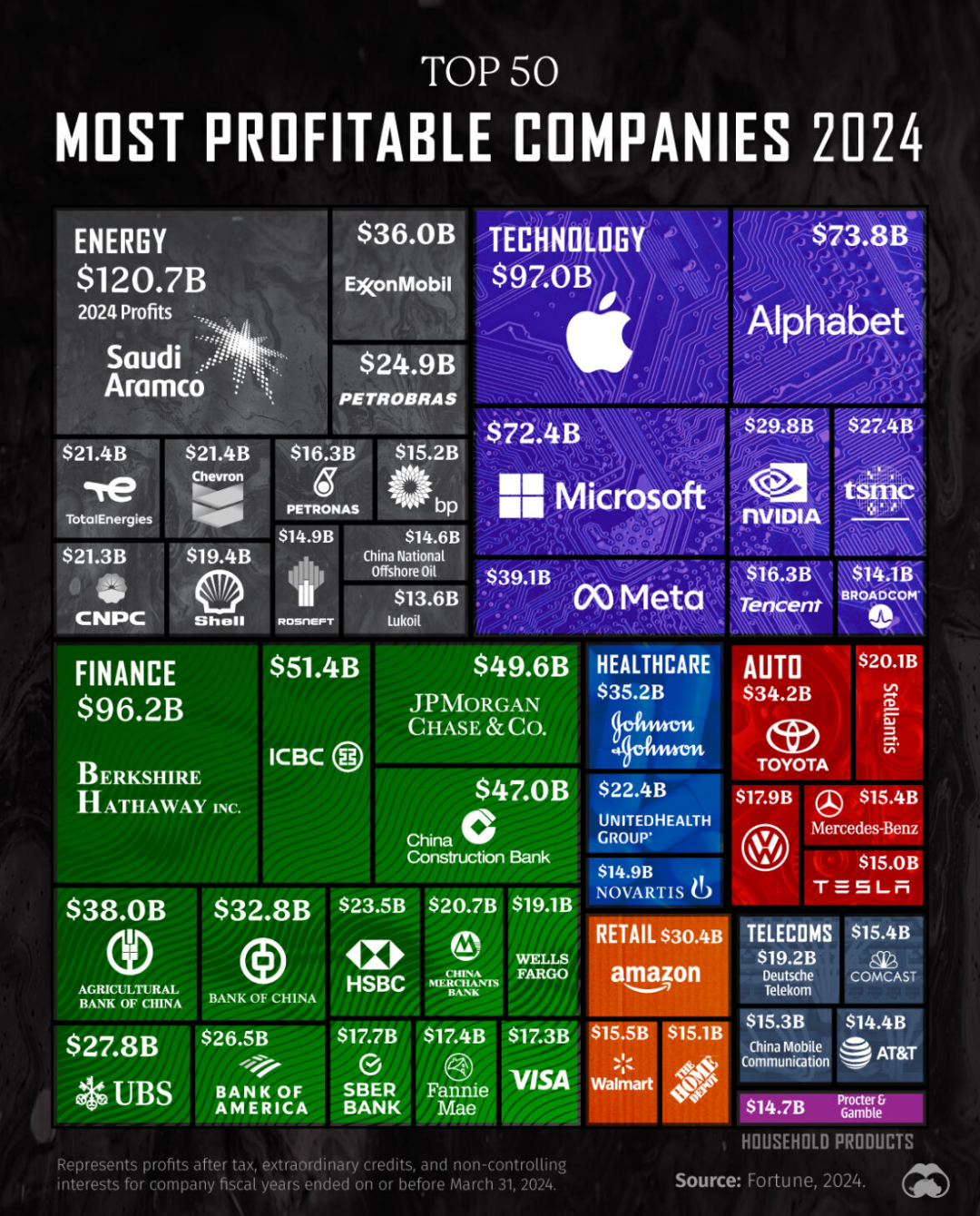
Is artificial intelligence a marvel of the modern world or a concept rooted in ancient philosophy?
The history of artificial intelligence spans centuries, with key milestones dating back to early philosophical ideas before reaching the technological wonders of today.
Understanding this timeline reveals how ancient Greek philosophy and the pioneering work of figures like Alan Turing and John McCarthy, who coined the term "Artificial Intelligence," shaped the foundation of AI.
Explore this timeline to uncover the transformative events and innovations, from the introduction of the Turing Test to the birth of the first neural network computer. By following AI's past, we gain valuable insights into its future potential.
How has AI evolved through history? Keep reading to find out.
Early Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
The concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be traced back to the 1700s, where the seeds of AI were sown through the philosophical musings of ancient Greek philosophers. These early thinkers speculated about the nature of intelligence and the possibility of creating artificial beings, laying the groundwork for future exploration and innovation.
In 1942, a pivotal development occurred when Alan Turing designed the Bombe machine. This machine was instrumental in deciphering German communications during World War II, showcasing the potential of machines to perform complex tasks. Turing's work during this period was foundational, proving that machines could be designed to solve problems that were previously thought to require human intelligence.
By 1950, Turing further solidified his legacy by proposing the Turing Test, a method to evaluate a machine's ability to exhibit intelligent behavior indistinguishable from that of a human. This test became a landmark in AI history, setting a benchmark for machine intelligence and sparking debates that continue to this day.
In 1955, the term "Artificial Intelligence" was coined by John McCarthy, a key figure in AI history. McCarthy's vision was to create machines that could simulate human intelligence, and his work laid the foundation for the AI field as we know it today.
The following year, in 1956, McCarthy organized the first AI conference, known as the Dartmouth Conference. This event is often regarded as the birth of AI as a field of study. It brought together leading thinkers to discuss and define the potential and direction of AI research, marking the beginning of AI's journey from theoretical speculation to a structured scientific discipline.
The Birth of AI: 1950s and 1960s
The 1950s and 1960s marked the emergence of artificial intelligence as a formalized field, driven by groundbreaking developments and visionary minds.
In 1950, Alan Turing published "Computing Machinery and Intelligence," introducing the concept of the Turing Test. This test was designed to measure a machine's ability to exhibit human-like intelligence, becoming a fundamental benchmark for AI research.
1951 saw the development of the first neural network computer, a significant leap in AI's ability to process information. This advancement laid the groundwork for future innovations in machine learning and neural networks, which continue to evolve today.
In 1955, John McCarthy coined the term "artificial intelligence," formalizing the field and setting the stage for dedicated research and exploration. McCarthy's contribution was pivotal, as it helped to delineate AI as a distinct area of study, separate from general computer science.
The 1960s witnessed further advancements, starting with General Motors' implementation of Unimate in 1961. Unimate was the first industrial robot, revolutionizing manufacturing processes and demonstrating AI's potential in automation and industry.
In 1965, the creation of ELIZA, the first chatbot, showcased AI's ability to simulate conversation and interact with humans. ELIZA's development was a precursor to modern conversational AI technologies, such as virtual assistants and chatbots.
By 1969, Shakey emerged as the first mobile robot capable of reasoning about its actions. Shakey's development was a testament to AI's growing complexity and ability to perform tasks autonomously.
- 1950: Alan Turing introduces the Turing Test
- 1951: First neural network computer developed
- 1955: Term "artificial intelligence" coined by John McCarthy
- 1961: General Motors uses Unimate, the first industrial robot
- 1965: ELIZA, the first chatbot, created
- 1969: Shakey, the first mobile robot, developed
These milestones underscore the rapid evolution of AI during this era, setting the foundation for future innovations and applications.
The Rise of AI: 1970s to 1990s
The period from 1970 to 1990 was a transformative era for artificial intelligence, marked by significant advancements and technological milestones.
In 1970, Japanese researchers made a significant breakthrough with the development of WABOT-1, the first anthropomorphic robot. This robot could perform tasks such as playing music and communicating in Japanese, showcasing AI's potential to mimic human-like capabilities.
The 1980s ushered in the era of expert systems, with XCON leading the charge as the first commercial expert system. Developed for Digital Equipment Corporation, XCON was used to configure orders of computer systems and demonstrated AI's utility in solving complex, real-world problems.
By 1991, the U.S. military had developed DART (Dynamic Analysis and Replanning Tool) to optimize logistics during the Gulf War. DART's implementation illustrated AI's strategic importance in military operations, enabling efficient resource allocation and planning.
A landmark achievement occurred in 1997 when IBM's DeepBlue defeated world chess champion Garry Kasparov. This victory underscored AI's growing capability to outperform humans in specific intellectual tasks, marking a pivotal moment in AI history.
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1970 | WABOT-1, the first anthropomorphic robot, developed |
| 1980s | XCON, the first commercial expert system, implemented |
| 1991 | U.S. military creates DART for logistics optimization |
| 1997 | IBM’s DeepBlue defeats chess champion Garry Kasparov |
These milestones highlight the rapid evolution of AI technologies during this era, illustrating both the challenges and the potential of AI to revolutionize various domains.
AI Breakthroughs in the New Millennium
The new millennium has witnessed remarkable advancements in artificial intelligence, reshaping everyday life and pushing the boundaries of what machines can achieve.
What was introduced in 2002 that marked a significant AI consumer product? The Roomba vacuum robot by iRobot was introduced. This innovative product demonstrated AI's ability to perform practical tasks autonomously, revolutionizing home cleaning by allowing consumers to automate mundane chores.
When did Apple's Siri debut, and what was its significance? Siri was launched in 2008. As a pioneering virtual assistant, Siri showcased AI's ability to understand and respond to natural language, setting the stage for more sophisticated voice-activated technologies.
What AI system made headlines in 2011? IBM Watson. Watson gained fame for winning the game show Jeopardy!, illustrating AI's capacity to process and analyze vast amounts of information quickly, with potential applications in fields like healthcare and finance.
Which AI-powered device did Amazon release in 2014? Amazon's Alexa. This smart speaker expanded the use of AI in households, providing users with a convenient way to control smart home devices, access information, and entertain themselves through voice commands.
Who became the first robot citizen in 2016? Sophia. Sophia's creation marked a milestone in human-robot interaction, as she was granted citizenship by Saudi Arabia, highlighting the potential for AI to engage with humans on a societal level.
What was Amper's contribution to AI in 2017? Amper, an AI music composer, was introduced. Amper demonstrated AI's creative capabilities, generating original music compositions and challenging traditional notions of artistry and creativity.
What significant AI model was launched in 2020? GPT-3 by OpenAI. As one of the most advanced language models, GPT-3 showcased impressive text generation capabilities, impacting industries reliant on content creation, customer service, and more.
- 2002: Introduction of the Roomba vacuum robot
- 2008: Launch of Apple's Siri
- 2011: IBM Watson wins Jeopardy!
- 2014: Amazon introduces Alexa
- 2016: Sophia becomes the first robot citizen
- 2017: Introduction of Amper, AI music composer
- 2020: Release of GPT-3 language model
These breakthroughs illustrate AI's rapid evolution and its profound impact on various aspects of daily life, from automating tasks to enhancing human creativity and interaction.
The Future of AI and Its Impact
What is the projected value of the AI market by 2030? The AI market is projected to grow to $826 billion. This growth reflects the increasing demand for AI technologies across industries, driven by advancements in machine learning, data analysis, and automation. As businesses strive for efficiency and innovation, AI's role is expected to expand, influencing economic landscapes globally.
How prevalent is AI expected to be in organizations by 2024? AI is anticipated to be integrated into 72% of organizations. This widespread adoption highlights AI's transformative potential in enhancing productivity, decision-making, and customer experiences. As AI becomes more accessible, organizations across sectors will increasingly rely on these technologies to maintain competitive advantages.
What are the key future trends in AI? The democratization of AI, increased regulations, and an emphasis on ethical considerations are pivotal. Democratization involves making AI tools and resources available to a broader audience, fostering innovation and inclusivity. However, as AI's influence grows, so does the need for regulations to ensure responsible use and mitigate risks. Ethical considerations will become central, guiding the development of AI systems that prioritize fairness, transparency, and accountability.
What challenges might arise with these trends? Open-source AI initiatives and regulatory challenges could emerge. While open-source AI promotes collaboration and innovation, it also raises concerns about security and misuse. Regulatory frameworks must balance fostering innovation with safeguarding public interests, posing a complex challenge for policymakers and industry leaders alike.
Final Words
From the foundations set by early philosophers to the pioneering work of Alan Turing and John McCarthy, the history of artificial intelligence timeline reveals a fascinating journey.
The 1950s and 1960s saw groundbreaking creations like the Turing Test, the first neural network computer, and innovations such as Unimate and ELIZA.
Fast forward to the 1970s and 1990s, AI made strides with anthropomorphic robots and expert systems, culminating in DeepBlue's chess victory.
The new millennium brought AI into everyday lives with Roomba and Siri, while GPT-3 sparked new possibilities.
The future of AI holds promise with projections of significant market growth and wider adoption, coupled with evolving ethical considerations.
AI continues to shape the world, offering remarkable opportunities for advancement and innovation.