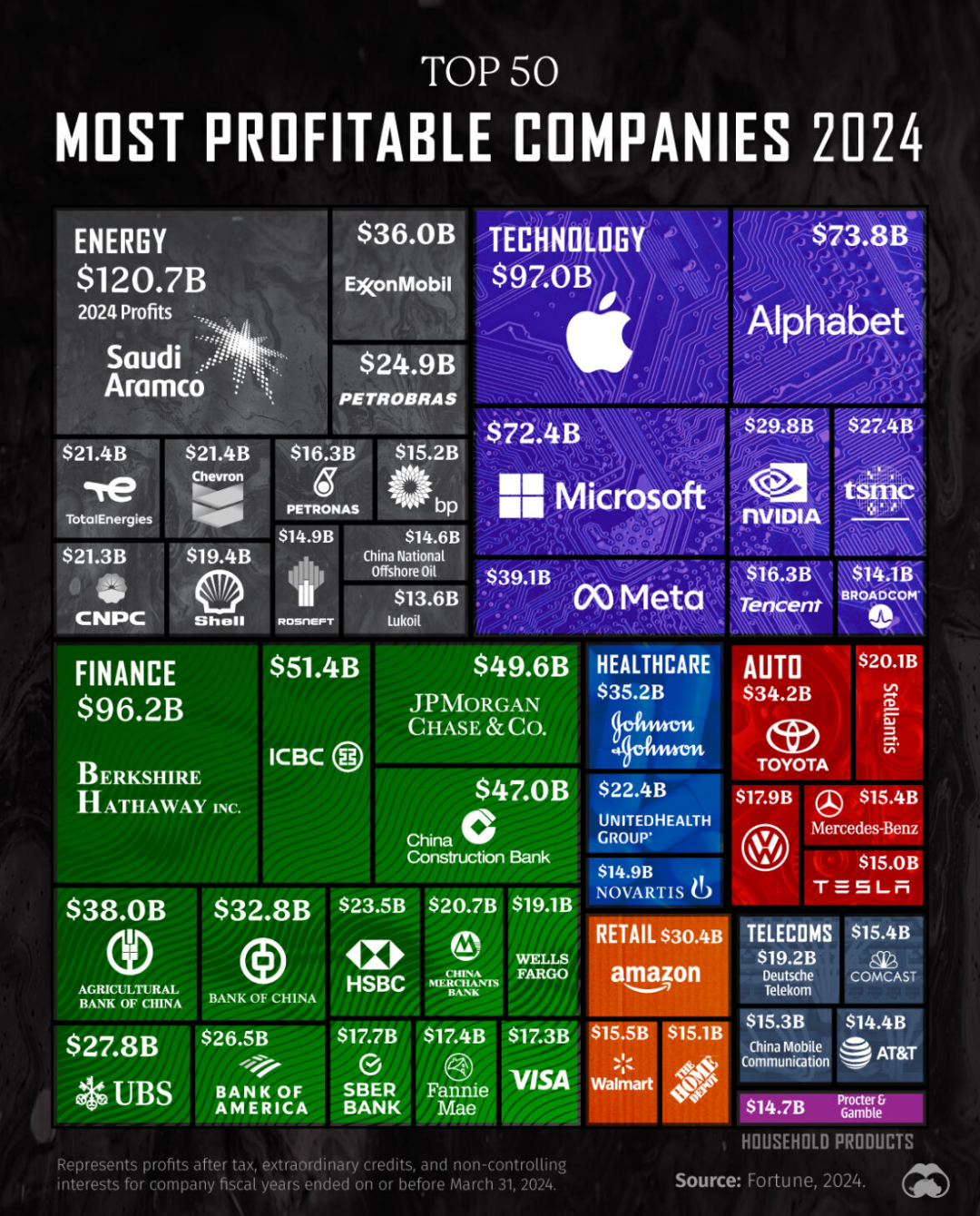
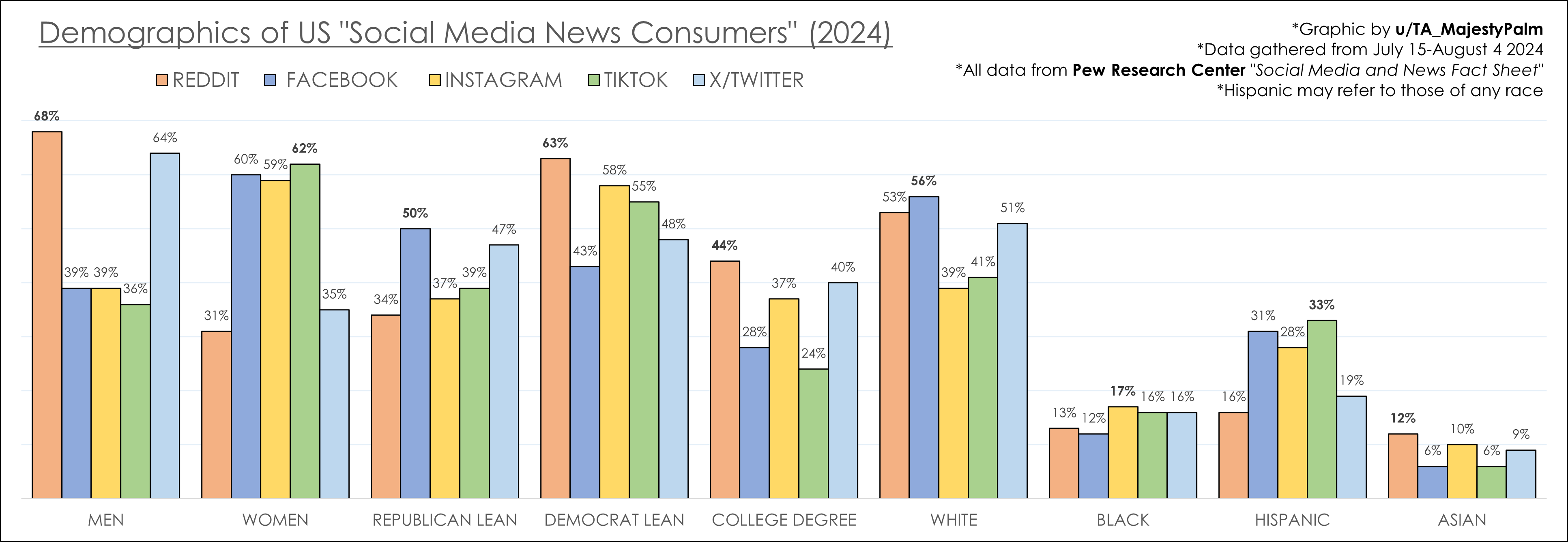
What if you could predict your future just by knowing where you were born? Life expectancy at birth reveals staggering contrasts across continents, spotlighting intriguing patterns that affect our global society.
In this exposé, we'll uncover the fascinating insights of life expectancy on each continent, guided by historical data and recent trends. By comparing average figures and exploring underlying disparities, we can gain a deeper understanding of the factors shaping longevity worldwide.
So, where does your birthplace put you in the longevity spectrum? Get ready to explore these captivating insights.
Life Expectancy at Birth: A Continental Overview
Life expectancy at birth is a crucial indicator of a population's overall health and well-being. It reflects the average number of years a newborn is expected to live, assuming current mortality rates remain constant. Comparing life expectancy by continent reveals significant insights into global health disparities and progress. In 2013, Oceania led with an average life expectancy of 78 years, followed closely by Europe at 77 years. The Americas and Asia reported 75 and 73 years, respectively. Africa lagged behind with an average of 60 years. These figures underscore the impact of factors such as healthcare access, economic conditions, and social structures on longevity.
Disparities in life expectancy across continents have persisted over the years, driven by varying levels of development and resources. For instance, Monaco, located in Europe, boasts the highest life expectancy at 87.01 years as of 2023, while Chad in Africa records one of the lowest at 49 years. These extremes highlight the stark contrast in living conditions and healthcare quality. Global life expectancy trends show gradual improvements, yet the pace differs significantly between regions. Africa has seen notable advancements, but it still trails behind other continents. Understanding these variations is vital for addressing health inequities and fostering sustainable development worldwide.
Continent | Average Life Expectancy (2013)
— | —
Europe | 77
Americas | 75
Asia | 73
Oceania | 78
Africa | 60
Factors Influencing Life Expectancy by Continent
Economic development and healthcare access are pivotal in shaping life expectancy across continents. How does economic development impact life expectancy? Countries with higher economic development typically have more resources to invest in healthcare infrastructure, leading to better medical services and preventive care. This is evident in Europe and the Americas, where robust healthcare systems contribute to higher life expectancy. Conversely, in regions like Africa, limited economic resources result in inadequate healthcare facilities, hindering life expectancy gains.
What societal and biological factors influence longevity? Societal factors such as education levels and gender roles play a significant role. Higher education often correlates with better health literacy and access to healthcare services. Gender differences also impact longevity, with women generally living longer than men due to biological and lifestyle factors. In many African and Asian societies, traditional gender roles can limit women's access to healthcare, affecting overall life expectancy. Biological factors, including genetics, further contribute to differences, with some populations having inherent predispositions to certain health conditions.
Environmental quality and lifestyle choices are crucial determinants of life expectancy. How do these factors affect longevity? Clean air, safe drinking water, and nutritious diets are essential for maintaining health. In regions with poor environmental conditions, such as parts of Africa and Asia, life expectancy is adversely affected by pollution and inadequate sanitation. Lifestyle choices, including diet and physical activity, also influence longevity. For example, the Mediterranean diet prevalent in parts of Europe is associated with longer life expectancy due to its emphasis on fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.
- Economic development
- Healthcare access
- Education levels
- Environmental quality
- Diet and lifestyle choices
Historical and Projected Trends in Global Life Expectancy
How has global life expectancy changed over time? Historically, life expectancy has seen remarkable changes, evolving from below 40 years in the 1800s to significantly higher figures today. This dramatic improvement can be attributed to advancements in medicine, public health initiatives, and improved living conditions. For instance, the introduction of vaccines and antibiotics has drastically reduced mortality rates from infectious diseases. The 20th century marked a pivotal era with the global life expectancy rising steadily, driven by innovations in healthcare and better nutrition. What are some key milestones? Notable milestones include the eradication of smallpox, the development of penicillin, and the widespread adoption of sanitation practices, all contributing to increased survival rates and longevity.
What are the future projections for life expectancy? Predictions indicate a continued upward trajectory in global life expectancy, fueled by ongoing medical advancements and enhanced health awareness. The World Health Organization anticipates further gains, particularly in regions like Africa, where life expectancy increased by 10.3 years from 2000 to 2016. Future improvements are expected to stem from personalized medicine, technological innovations in healthcare, and global health policies aimed at reducing disparities. What potential developments could impact life expectancy? Emerging challenges such as climate change, antibiotic resistance, and lifestyle-related diseases could influence future trends, necessitating adaptive strategies to sustain improvements.
- Development of vaccines
- Eradication of smallpox
- Introduction of antibiotics
- Advances in sanitation
- Rise of public health systems
Life Expectancy Disparities Among Continents
What are the primary disparities in life expectancy across continents? The disparities in life expectancy among continents are pronounced, with Africa having the lowest figures and Oceania boasting the highest. These differences are primarily driven by variations in health infrastructure, educational opportunities, living conditions, and economic development. While countries in Europe and Oceania enjoy higher average life expectancies, many African nations struggle with significantly lower figures, reflecting the uneven distribution of resources and healthcare access worldwide.
How do specific regions compare in terms of life expectancy? In regions like Europe and Oceania, life expectancy is generally higher due to well-established healthcare systems, better living conditions, and higher standards of education. For instance, countries such as Monaco and Australia consistently rank at the top with life expectancies exceeding 80 years. On the other hand, African countries, particularly those in sub-Saharan regions, face challenges such as limited access to medical care and lower economic development, resulting in life expectancies that can be as low as 49 years, as seen in Chad. These regional differences highlight the impact of socioeconomic factors on health outcomes.
What demographic and social factors influence these disparities? Demographic influences, such as age distribution and population density, play a crucial role in shaping life expectancy. Regions with younger populations, like many African countries, often experience higher mortality rates due to factors such as infectious diseases and maternal health challenges. Social factors, including gender roles and cultural practices, also contribute to disparities. For instance, gender disparities in healthcare access can lead to differences in life expectancy between men and women. Additionally, societal norms that affect lifestyle choices, such as diet and physical activity, further influence longevity across different regions.
Continent | Life Expectancy Range
— | —
Europe | 77-87
Americas | 75-81
Asia | 73-84
Oceania | 78-83
Africa | 49-60
Life Expectancy by Continent: Recent Data and Trends
How has life expectancy in Africa changed recently? Africa has shown improvements in life expectancy, yet it remains the continent with the lowest figures globally. As of 2023, the average life expectancy in Africa is still significantly lower compared to other continents, mainly due to ongoing challenges such as healthcare access, economic disparities, and infectious diseases. However, targeted health interventions and international aid have contributed to gradual increases over the past decade. Countries like Rwanda and Ethiopia have seen notable progress due to improved healthcare systems and public health initiatives.
What is the current state of life expectancy in Europe? Europe continues to boast some of the highest life expectancy figures worldwide. Stability in healthcare systems, economic prosperity, and a high standard of living contribute to this trend. Monaco, for example, leads globally with an impressive life expectancy, reflecting the region's healthcare quality and living conditions. Most European countries maintain life expectancies well above 80 years, a testament to their robust healthcare infrastructures and health-promoting lifestyles.
Where do Asia and Oceania stand in terms of life expectancy? Asia presents a diverse picture, with countries like Japan and Singapore achieving high life expectancy rates due to advancements in healthcare and technology. Meanwhile, countries with rapidly developing economies, such as India and China, are seeing improvements as they invest more in healthcare and infrastructure. Oceania, particularly Australia and New Zealand, consistently ranks high in life expectancy due to their comprehensive healthcare systems and healthy living environments. These regions benefit from a combination of economic stability and access to quality healthcare services.
What are the trends in life expectancy in North and South America? North America, led by Canada, enjoys high life expectancy figures, attributed to advanced healthcare and high standards of living. The United States, while also high, faces challenges such as lifestyle diseases that impact overall longevity. South America's life expectancy varies, with countries like Chile and Uruguay performing well due to effective healthcare policies. However, economic disparities and political instability in some regions pose challenges to further improvements. These trends highlight the importance of addressing health inequalities and promoting sustainable development across the Americas.
Final Words
Exploring life expectancy at birth by continent reveals how diverse and complex these figures can be.
Continents like Europe, the Americas, and Oceania consistently show higher life expectancies, thanks to better healthcare and living conditions.
In contrast, Africa, despite improvements, still faces challenges due to socioeconomic factors.
By understanding the factors influencing life expectancy, from healthcare access to environmental conditions, there's potential to improve global outcomes.
Looking ahead, continued advancements suggest a promising rise in global life expectancy, offering hope for longer, healthier lives across all continents.