What can the adult literacy rates of each state reveal about the United States from 2012 to 2017?
The U.S. PIAAC Skills Map and the American Community Survey provide a detailed analysis of adult literacy rates, involving over 12,000 U.S. adults aged 16 to 74. This data categorizes literacy into three levels, offering a snapshot of literacy skills across the nation during this period.
Understanding these literacy levels is crucial as it helps highlight regional disparities, influences from socio-economic factors, and the effectiveness of educational policies. By examining these trends, we can grasp the challenges faced by certain regions and the potential pathways toward improving literacy in the future.
In sum, adult literacy rates serve as a mirror reflecting not only educational achievements but also societal and economic benchmarks.
Overview of Adult Literacy Rates by State (2012-2017)
Adult literacy rates in the United States from 2012 to 2017 have been extensively studied through the U.S. PIAAC Skills Map and the American Community Survey. These surveys collectively involved over 12,000 adults aged 16 to 74, providing a broad representation of the population's literacy skills. Literacy is assessed across three distinct levels: Level 1, indicating the lowest proficiency, Level 2, and Level 3, representing the highest proficiency. This classification allows for a nuanced understanding of literacy capabilities across the U.S. adult population, facilitating targeted educational interventions and policy-making.
Understanding adult literacy statistics during this period is crucial for identifying and addressing literacy challenges at the state level. The data reveals significant insights into how literacy rates vary across states, offering a comparative framework for evaluating educational outcomes. By analyzing this data, policymakers and educators can identify trends, such as which states have made progress in improving literacy rates and which have fallen behind. This understanding is essential for developing effective strategies to enhance literacy skills, thereby improving economic opportunities and quality of life for adults nationwide.
State Rankings and Literacy Trends (2012-2017)
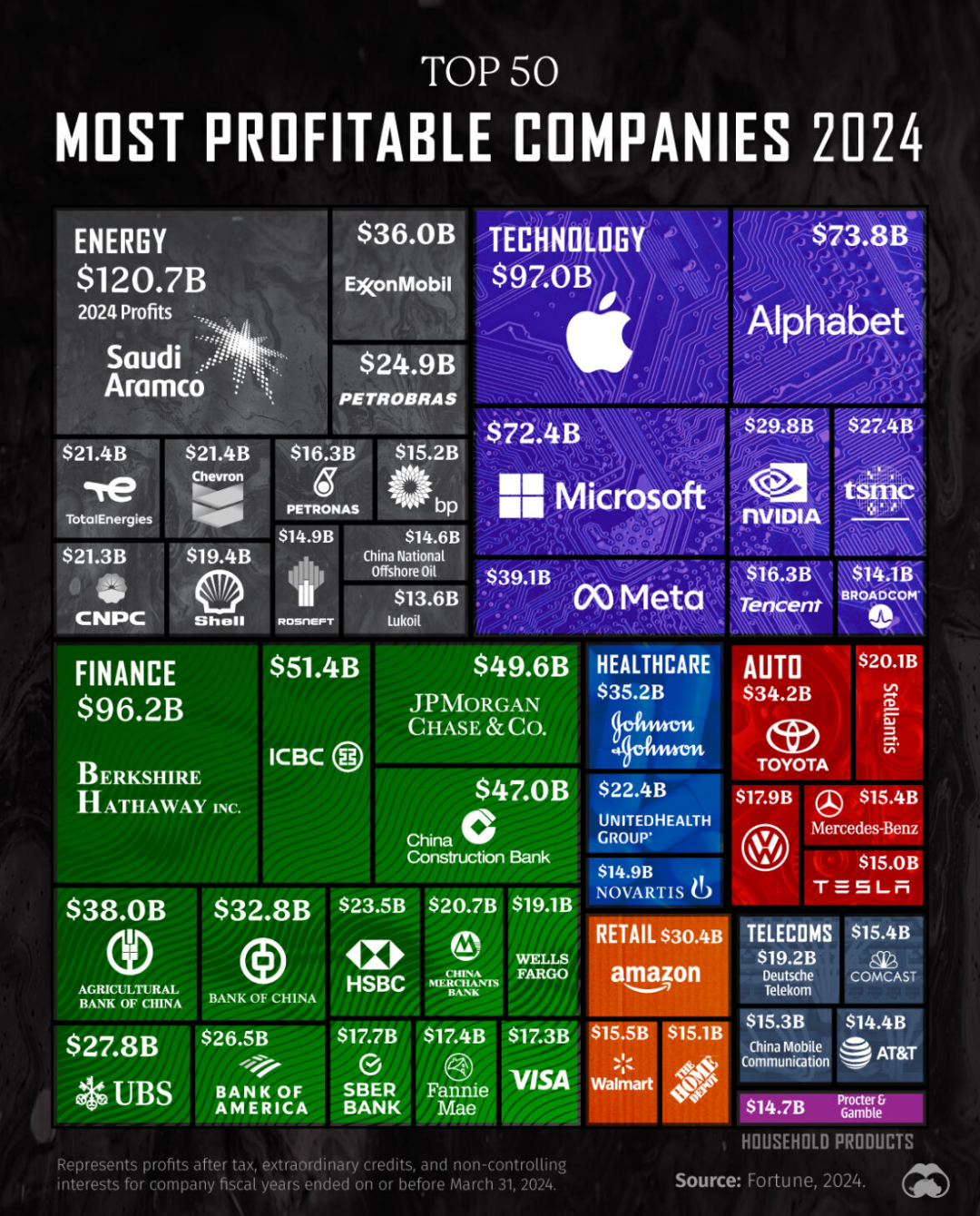
In the period from 2012 to 2017, literacy scores among U.S. adults varied significantly across states, as captured by the U.S. PIAAC Skills Map. The average literacy score for U.S. adults was 270 out of 500, marginally below the global average of 273. New Hampshire emerged as the leader with the highest literacy score of 278.9, while Nevada recorded the lowest at 254.9. This variation underscores the disparities in reading proficiency and educational outcomes across the nation. A closer look at the data reveals that states with higher scores generally have more robust educational systems and policies aimed at fostering literacy advancement. Conversely, lower-scoring states often face challenges such as limited educational resources and higher rates of socio-economic disadvantage.
- Highest Literacy Scores:
- New Hampshire: 278.9
- Minnesota: 276.8
- Vermont: 275.3
- Massachusetts: 274.7
- Connecticut: 273.5
- Lowest Literacy Scores:
- Nevada: 254.9
- California: 256.2
- Texas: 257.4
- New Mexico: 258.1
- Louisiana: 259.3
The implications of these rankings are profound. States with higher literacy scores often enjoy better economic outcomes, as literacy is closely linked to employment opportunities and income levels. These states are typically able to attract businesses that require a skilled workforce, thereby fostering economic growth. On the other hand, states with lower literacy scores may struggle with economic development and face challenges in breaking the cycle of poverty. Addressing these disparities requires targeted educational policies and investments that focus on improving literacy skills, particularly in underperforming states. This can lead to more equitable opportunities across the country and enhance overall national productivity.
Regional Disparities in Literacy Skills
Which regions have significant literacy challenges? The Southern states and those with high immigration levels are identified as having the lowest literacy levels between 2012 and 2017. These areas face notable literacy challenges, which are reflected in lower average literacy scores compared to other regions. Such disparities highlight the uneven distribution of educational resources and opportunities across the United States. Why is this important? Understanding these regional differences is crucial for developing targeted strategies to address literacy gaps and improve educational outcomes.
What factors contribute to these disparities? Several factors contribute to the literacy challenges faced by these regions. Socio-economic conditions, such as poverty and unemployment, often limit access to quality education and literacy programs. Additionally, high immigration levels can lead to language barriers that impede literacy development. The availability and quality of educational resources also vary significantly, with some regions lacking sufficient funding and infrastructure to support effective literacy education. Addressing these underlying causes requires a comprehensive approach, focusing on improving access to education, supporting language acquisition, and investing in community-based literacy initiatives.
Socio-Economic Factors Affecting Literacy Rates
How do literacy rates impact economic outcomes? Higher literacy rates are directly linked to better job opportunities and economic growth. Individuals with proficient literacy skills are more likely to secure employment in higher-paying jobs, which in turn boosts their economic stability and contributes to overall economic development. Why is this significant? In states where literacy rates are higher, there tends to be greater economic prosperity. These states often attract businesses that require a skilled workforce, resulting in more robust local economies. Conversely, lower literacy rates can hinder economic progress, leading to higher unemployment rates and limited economic growth.
What demographic factors influence literacy skills? Several key demographic factors play a role in shaping literacy rates. Age is a significant factor; younger adults often display higher literacy levels compared to older generations, likely due to more recent educational advancements and access to resources. Education level is another crucial determinant, as individuals with higher educational attainment generally possess better literacy skills. Immigration status also influences literacy rates, with immigrants often facing language barriers that can impact their literacy development. Understanding these demographic influences is essential for crafting policies and programs that aim to improve literacy rates and address the specific needs of diverse populations. Addressing these factors can lead to more equitable literacy outcomes and contribute to economic resilience and growth.
Educational Policies and Literacy Improvement Strategies
What educational policies have been implemented to improve literacy rates? Several key strategies and policies have been introduced across various states to tackle literacy challenges. These include:
- Adult Basic Education (ABE) Programs: Designed to equip adults with fundamental reading, writing, and math skills.
- Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act (WIOA): A federal initiative focusing on integrating adult education with workforce training to enhance employability.
- Family Literacy Programs: Targeting both adults and children to improve literacy rates through a family-centered approach.
- English Language Acquisition (ELA) Classes: Aimed specifically at immigrants to improve English proficiency and literacy.
- Digital Literacy Initiatives: Incorporating technology to teach essential digital skills alongside traditional literacy.
These policies reflect a comprehensive approach to improving literacy, addressing various dimensions from basic education to digital competency.
How effective are these policies in improving literacy rates? The impact of these policies has been mixed, with some states witnessing significant improvements while others continue to face challenges. States that have successfully integrated workforce training with literacy programs, like those under WIOA, report better employment outcomes and higher literacy rates. Family Literacy Programs have been particularly effective in creating a supportive learning environment, fostering intergenerational literacy improvements. However, the success of these initiatives largely depends on the availability of resources and the extent of community involvement. Digital Literacy Initiatives have gained momentum, providing adults with essential skills for the modern workforce, but disparities in access to technology can limit their reach. Overall, while these strategies have shown promise, ongoing evaluation and adaptation are crucial to address the diverse needs of adult learners and achieve widespread literacy improvements.
Literacy Programs and Initiatives
What types of literacy programs are available? Various literacy programs have been launched to enhance adult literacy skills across the United States, reflecting a diverse approach to tackling literacy challenges. Adult Basic Education (ABE) programs are a cornerstone, focusing on improving fundamental skills in reading, writing, and arithmetic. These programs are often complemented by English Language Acquisition (ELA) classes, which cater specifically to immigrants to help overcome language barriers and improve literacy. Additionally, Family Literacy Programs adopt a holistic approach, involving both adults and children to foster a culture of learning within families. Digital Literacy Initiatives have also gained prominence, integrating technology into the learning process to equip adults with essential digital skills needed in today’s workforce. These programs are supported by a mix of public funding and private sector partnerships, facilitating broader access and sustainability.
How successful are these programs in improving literacy rates? The success of literacy programs and initiatives has been mixed, with varying degrees of effectiveness across different states. Public and private partnerships have been pivotal in providing resources and support for these initiatives, yet challenges remain. What are the main challenges? One significant challenge is the uneven distribution of resources, which leads to disparities in program availability and quality. Digital Literacy Initiatives face hurdles in areas with limited access to technology, hindering their potential impact. Moreover, Family Literacy Programs require significant community involvement and support to be effective, which is not always feasible. Despite these challenges, states that have effectively integrated literacy programs with workforce development initiatives, such as those under the Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act (WIOA), report positive outcomes in employment and literacy rates. Continuous evaluation and adaptation of these programs are essential to address the diverse needs of adult learners and to improve literacy outcomes nationwide.
Future Outlook for Adult Literacy in the U.S.
What are the current challenges in adult literacy? Despite numerous efforts to improve literacy rates, challenges persist across the United States. Ongoing investment in literacy development is crucial, as many states continue to struggle with disparities in educational resources and access. Why is this important? Without addressing these foundational issues, achieving significant improvements in literacy rates remains difficult. Socio-economic factors such as poverty and unemployment further exacerbate these challenges, limiting the effectiveness of existing literacy programs. The need for targeted interventions that address both educational and economic barriers is evident, as these factors are deeply intertwined and impact the overall success of literacy initiatives.
What trends and innovations could shape the future of literacy development? Emerging trends and technologies present new opportunities for enhancing literacy skills. Digital learning platforms are gaining traction, offering flexible and accessible solutions for adult learners. These platforms can bridge gaps in traditional education systems by providing tailored learning experiences that cater to individual needs. How can technology help? By leveraging technology, educators can reach a broader audience and offer resources that were previously inaccessible. Furthermore, collaborative initiatives between public and private sectors are crucial in advancing state literacy efforts. These partnerships can drive innovation and investment in literacy programs, ensuring they are equipped to meet the evolving demands of the workforce and society. As these trends unfold, they hold the potential to reshape the landscape of adult literacy in the U.S., paving the way for more inclusive and effective educational strategies.
Final Words
Exploring the adult literacy rates by state from 2012-2017 reveals significant variations in literacy skills and highlights essential socio-economic influences.
States like New Hampshire lead in literacy scores due to effective policies, whereas regions with high immigration often face obstacles.
Such data underlines the need for comprehensive literacy initiatives and policies that address these disparities.
However, literacy improvements demand continuous effort and the adoption of emerging educational technologies.
The ongoing commitment to literacy development will bolster economic outcomes and provide equitable educational opportunities nationwide.
By addressing the underlying factors and prioritizing innovative strategies, the U.S. can foster a future where literacy is accessible to all.